Study the following phase diagram of substance x. – Delving into the study of phase diagrams, we embark on a journey to understand the intricate relationship between temperature, pressure, and the physical states of matter. Phase diagrams serve as invaluable tools in materials science, providing insights into the behavior of substances under varying conditions and enabling predictions of their properties.
The phase diagram of substance X, which we will examine in this exploration, presents a graphical representation of the equilibrium states of the substance. By analyzing its components, phase transitions, boundaries, and applications, we gain a comprehensive understanding of the substance’s behavior and its potential uses.
Phase Diagram Components: Study The Following Phase Diagram Of Substance X.
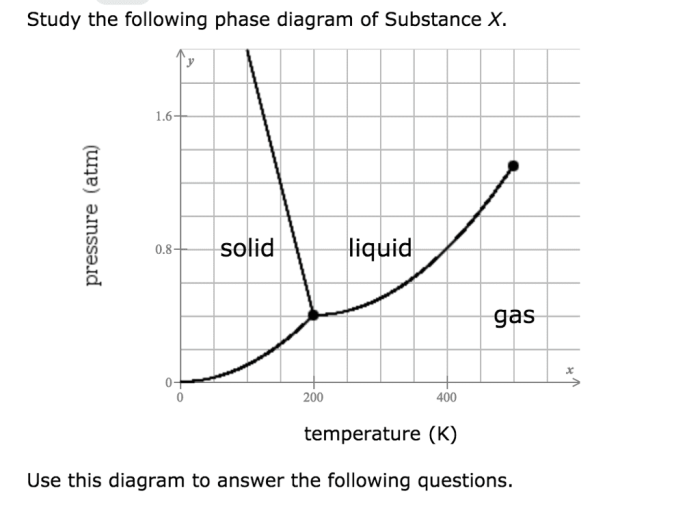
A phase diagram is a graphical representation of the thermodynamic conditions under which different phases of a substance can exist.
The axes of a phase diagram typically represent temperature and pressure. The phases represented on the diagram can include solids, liquids, gases, and mixtures of these phases.
The critical point is the point on the phase diagram where the liquid and gas phases become indistinguishable. The triple point is the point on the phase diagram where the solid, liquid, and gas phases can coexist in equilibrium.
Phase Transitions
Phase transitions are changes in the physical state of a substance. The different phase transitions shown on a phase diagram include melting, freezing, boiling, and condensation.
Melting occurs when a solid is heated to its melting point and turns into a liquid. Freezing occurs when a liquid is cooled to its freezing point and turns into a solid.
Boiling occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point and turns into a gas. Condensation occurs when a gas is cooled to its condensation point and turns into a liquid.
During a phase transition, the properties of the substance change. For example, when a solid melts, it becomes less dense and more fluid.
Phase Boundaries
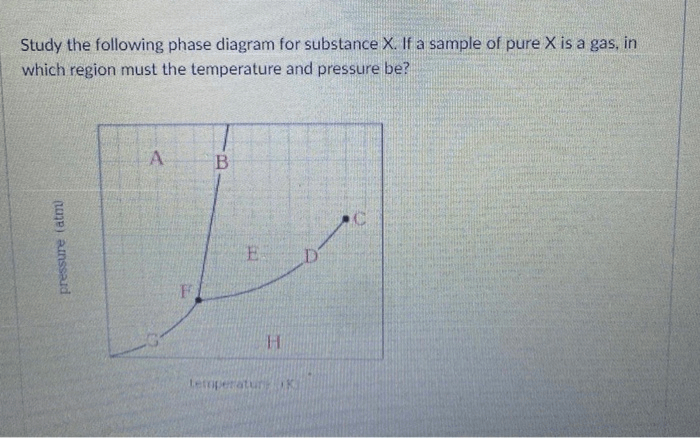
Phase boundaries are the lines on a phase diagram that separate the different phases. The slopes of the phase boundaries indicate the changes in temperature and pressure that are required to induce a phase transition.
For example, the slope of the solid-liquid phase boundary indicates the change in pressure that is required to induce melting at a given temperature.
The phase boundaries change with temperature and pressure. For example, the solid-liquid phase boundary moves to higher temperatures and pressures as the pressure increases.
Applications of Phase Diagrams
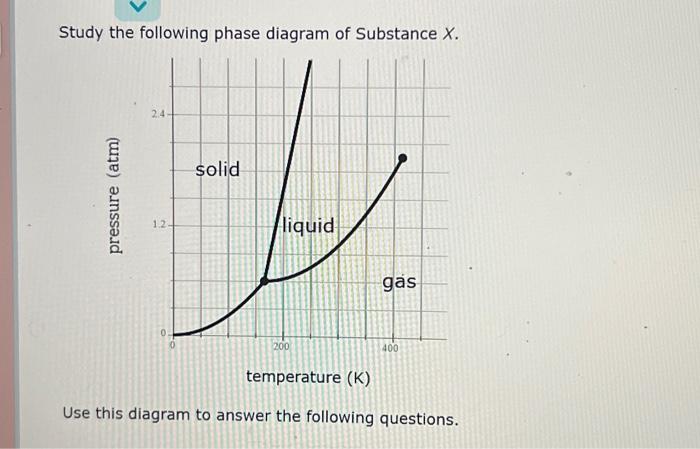
Phase diagrams are used in a variety of applications in materials science. For example, phase diagrams can be used to:
- Predict the behavior of materials under different conditions
- Design new materials with desired properties
- Understand the phase transitions that occur during materials processing
Phase diagrams are a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of materials. However, it is important to note that phase diagrams are only approximations of the real behavior of materials.
Expert Answers
What is a phase diagram?
A phase diagram is a graphical representation of the equilibrium states of a substance at different temperatures and pressures.
What information can be obtained from a phase diagram?
Phase diagrams provide information about the phase transitions, phase boundaries, and the stability of different phases of a substance under varying conditions.
How are phase diagrams used in materials science?
Phase diagrams are used in materials science to predict the behavior of materials, optimize processes, and design new materials with desired properties.