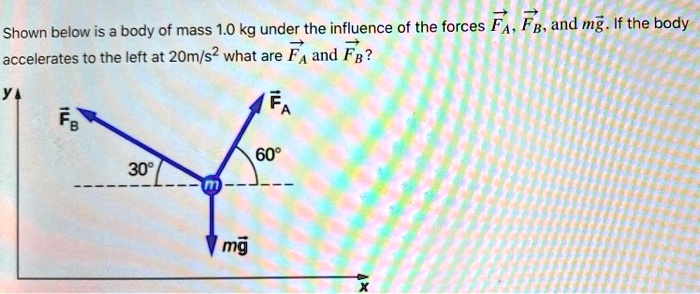
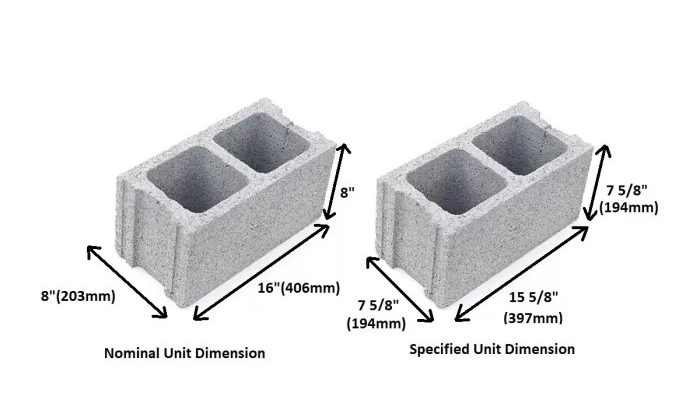
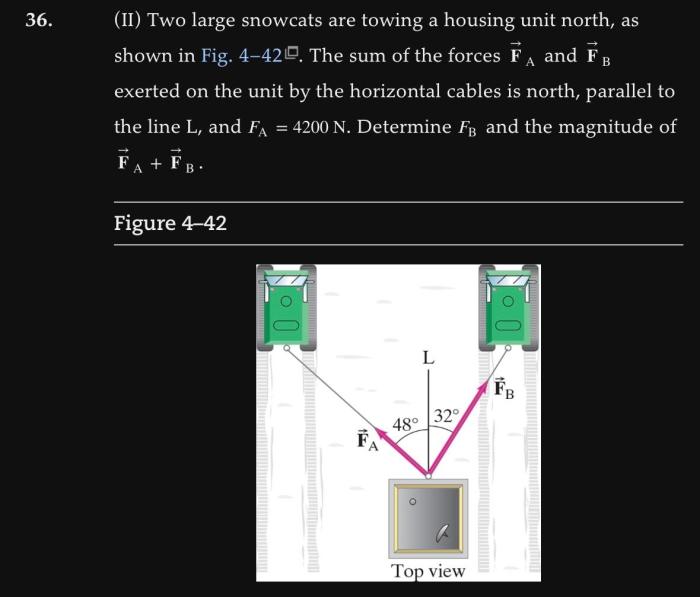
Two forces fa and fb are applied to an object – When two forces, Fa and Fb, are applied to an object, they interact in various ways, affecting its motion and equilibrium. This intricate interplay forms the cornerstone of our exploration, providing insights into the fundamental principles governing the behavior of objects under the influence of external forces.
As we delve into the intricacies of force interactions, we will uncover the concepts of resultant force, equilibrium conditions, and their practical applications. By examining real-world scenarios, we will witness the tangible effects of these forces on objects, solidifying our understanding of their significance in shaping the physical world around us.
Two Forces: Fa and Fb: Two Forces Fa And Fb Are Applied To An Object
Forces are physical quantities that describe the interaction between objects. They have both magnitude and direction, and their units of measurement are Newtons (N). In this context, we consider two forces, Fa and Fb, acting on an object.
Fa is applied in the positive x-direction, while Fb is applied in the negative x-direction.
Resultant Force
When two forces are applied to an object, the resultant force is the vector sum of the individual forces.
- If Fa and Fb are applied in the same direction, the resultant force is the sum of the two forces.
- If Fa and Fb are applied in opposite directions, the resultant force is the difference between the two forces.
Equilibrium
An object is in equilibrium when the net force acting on it is zero. For an object under the influence of Fa and Fb, equilibrium occurs when:
- Fa = Fb (if forces are in opposite directions)
- Fa = 0 or Fb = 0 (if forces are in the same direction)
There are three types of equilibrium:
- Stable equilibrium: The object returns to its equilibrium position after a small displacement.
- Unstable equilibrium: The object moves away from its equilibrium position after a small displacement.
- Neutral equilibrium: The object remains in its equilibrium position after a small displacement.
Applications
Two forces, Fa and Fb, are involved in numerous real-world applications:
- Pulling and pushing objects
- Friction between surfaces
- Elasticity and spring forces
- Gravitational forces between objects
Graphical Representation
| Force | Magnitude | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Fa | F | +x |
| Fb | F | -x |
| Resultant Force | 2F (same direction) | 0 (opposite directions) |
Advanced Concepts, Two forces fa and fb are applied to an object
In advanced mechanics, force vectors and their components are used to analyze forces acting on objects.
Newton’s laws of motion can be applied to objects under the influence of Fa and Fb to determine their acceleration and motion.
FAQ Summary
What is the resultant force when Fa and Fb act in the same direction?
The resultant force is the vector sum of Fa and Fb, resulting in a force of greater magnitude in the same direction.
What conditions must be met for an object to be in equilibrium?
For equilibrium, the net force acting on the object must be zero, meaning the vector sum of all forces, including Fa and Fb, must be zero.
How do Fa and Fb affect an object’s motion?
The resultant force of Fa and Fb determines the object’s acceleration. If the resultant force is non-zero, the object will accelerate in the direction of the resultant force.