Embark on an illuminating journey with our protein synthesis and mutations review sheet answer key, an authoritative resource that unravels the intricate mechanisms of protein synthesis and the impact of mutations on this vital process. This comprehensive guide empowers you with a profound understanding of the molecular foundations of life.
Delve into the intricacies of protein synthesis, tracing the remarkable transformation of genetic information encoded in DNA into functional proteins. Uncover the pivotal roles of DNA and RNA in this intricate dance, and witness the precise choreography of molecular machinery as it orchestrates the assembly of amino acids into complex protein structures.
Protein Synthesis
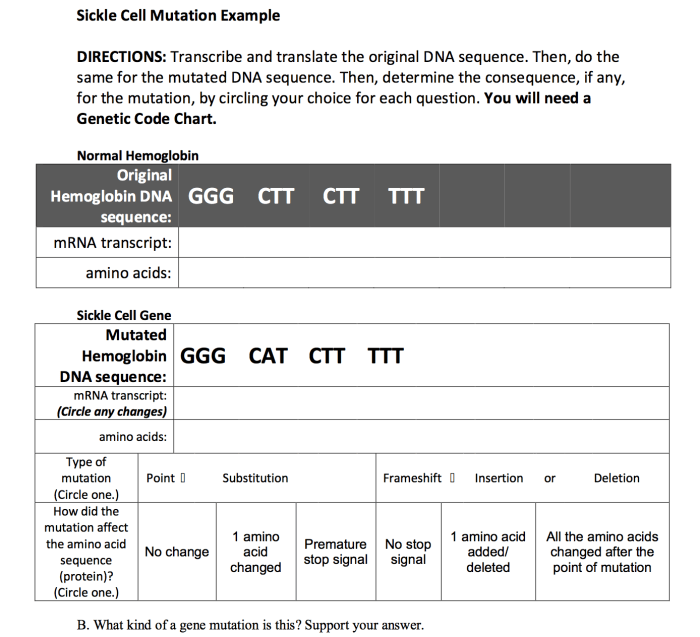
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells create proteins. Proteins are essential for life, as they play a role in a wide range of cellular functions, including metabolism, growth, and repair. The process of protein synthesis is complex and involves several steps.
Transcription
The first step in protein synthesis is transcription. During transcription, the DNA in the nucleus is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The mRNA molecule then travels to the cytoplasm, where it will be used to create a protein.
Translation, Protein synthesis and mutations review sheet answer key
The second step in protein synthesis is translation. During translation, the mRNA molecule is read by a ribosome, which is a large complex of RNA and proteins. The ribosome reads the mRNA molecule in groups of three nucleotides, called codons.
Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid. The ribosome then assembles the amino acids into a polypeptide chain, which is the final product of protein synthesis.
Mutations: Protein Synthesis And Mutations Review Sheet Answer Key
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence of an organism. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental factors such as radiation and chemicals, and errors that occur during DNA replication. Mutations can have a wide range of effects on an organism, depending on the type of mutation and the location of the mutation in the DNA sequence.
Types of Mutations
- Point mutationsare changes in a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence.
- Insertionsare additions of one or more nucleotides to the DNA sequence.
- Deletionsare removals of one or more nucleotides from the DNA sequence.
Effects of Mutations on Protein Synthesis
Mutations can have a variety of effects on protein synthesis. Some mutations may have no effect on protein synthesis, while others may result in the production of a non-functional protein. The effects of a mutation on protein synthesis will depend on the type of mutation and the location of the mutation in the DNA sequence.
- Point mutationscan result in the production of a non-functional protein if the mutation changes the codon for an amino acid. For example, a mutation that changes the codon for the amino acid glycine to the codon for the amino acid valine will result in the production of a protein that contains valine instead of glycine.
- Insertionsand deletionscan also result in the production of a non-functional protein if the mutation changes the reading frame of the mRNA molecule. The reading frame is the grouping of codons that are read by the ribosome. If an insertion or deletion changes the reading frame, the ribosome will read the mRNA molecule incorrectly, which will result in the production of a non-functional protein.
Detailed FAQs
What is the role of DNA in protein synthesis?
DNA serves as the blueprint for protein synthesis, carrying the genetic code that determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins.
How do mutations affect protein synthesis?
Mutations can alter the DNA sequence, potentially leading to changes in the amino acid sequence of proteins, which can disrupt their structure and function.
What are the different types of mutations?
Mutations can be classified into various types, including point mutations, insertions, deletions, and inversions, each with distinct effects on the DNA sequence.